What's New in OMNEST 5.1.1
This release significantly improves and builds upon functionality introduced in version 5.0, and also raises the bar in other areas.
Highlights:
- A much-improved Qtenv that now replaces Tkenv as the default runtime GUI.
- Support for smooth custom animation and video recording.
- Better support for simulation campaigns in managing and performing a large number of runs and in result recording/processing.
- Experimental support for SQLite-based result files.
- Updated data export tools.
- Updated toolchain and libraries on Windows including 64-bit Windows support.
- Updated Eclipse base for the IDE.
Core:
-
Support for smooth custom animations. The goal was to allow models to visualize their operation using sophisticated animations while the simulation is running under a GUI (Qtenv). The key idea is that refreshDisplay() is called repeatedly at a reasonable rate to render frames. refreshDisplay() knows the animation position from the simulation time (which is now interpolated between events) and the "animation time", a variable also made accessible to the model. Animation-to-simulation speed ratio (sec/simsec) is determined by an "animation speed" variable (or rather, several such variables) that can be set explicitly from code. Different animation speeds can be chosen dynamically to adapt the animation to the current time scale of the interesting events or processes in the simulation. Animations that need to take place in zero simulation time are supported with "holds", i.e. holding up the simulation for a certain animation time period. The actual playing speed of the resulting animation can be controlled in Qtenv using the "Speed" slider on the toolbar. Note that this feature is only available in Qtenv (and not in Tkenv which is more-or-less in maintenance mode from now on).
-
If a model implements such full-blown animations for a compound module that OMNEST's default animations (message sending/method call animations) become a liability, they can now be programmatically turned off for that module with a setBuiltinAnimationsAllowed(false) call.
-
Support for self-refreshing figures. cFigure now has a refreshDisplay() method which is called on every display refresh as long as the containing canvas is open in the GUI. Overriding that method in custom figure classes allows the figure to update itself according to the state of the simulation. The self-refreshing feature is especially useful for figures that implement various meters, gauges, plots or charts, because this way they don’t require an additional helper module to update them. Note this feature is only available in Qtenv.
-
Custom figure classes are now registered using Register_Figure(), not with Register_Class(). This allows for more flexibility and a cleaner handling of C++ namespaces.
-
The stacking order of figures is now jointly determined by the child order and a new runtime-settable cFigure member called zIndex, with the latter taking priority. In @figure properties in NED files, "zIndex" replaces "childZ" which was only used at parse time but not stored in figures afterwards.
-
A figure can now have a tooltip text set.
-
A figure can now be associated with a simulation object, for example a module or a packet. Association means that the figure more-or-less "stands for" (or visually represents) the other object in the GUI. For example, when the user clicks or double-clicks the figure under Qtenv, the associated object is focused or opened in the GUI. The figure also "inherits" the tooltip of its associated object, provided it does not have its own tooltip.
-
For text figures, one can now optionally turn on a "halo", which makes the text more readable on all backgrounds.
-
Support has been added to load custom images for use by cImageFigure/cIconFigure and in display strings (cEnvir::loadImage()). It is also possible now to programmatically add new directories to the image path (cEnvir::appendToImagePath()).
-
The dimensions of images used by cImageFigure/cIconFigure can now be determined programmatically (getImageNaturalWidth() / getImageNaturalHeight() methods).
-
Support for measuring the text has been added to cTextFigure and cLabelFigure (getBounds() method). Note that getBounds() assumes zoom level 1.0.
-
Support for accessing the coordinates of auto-layouted submodules (cEnvir:: getSubmoduleBounds()). This functionality is needed by some visualizers in INET, where nodes of a wired network are typically not explicitly placed.
-
In cObject and subclasses, info() has been renamed to str(). The old method still exists and delegates to the new one. The detailedInfo() method has been deprecated due to lack of usefulness.
-
In NED statistic declarations (@statistic), signal names in the "source" attribute can now be qualified with the name of a submodule. This will cause the signal listener to be added to the given submodule instead of the module containing the @statistic. Example: @statistic[foo](source=a.b.foo). Note that there is no syntax to specify modules above or outside the one containing the @statistic, as that would limit the module’s reusability (encapsulation violation).
-
In cModule, the arrived() method has been made public API. arrived() is invoked as part of the send() protocol, and its default version inserts the message into the FES after some bookkeeping. Overriding arrived() allows one to perform custom processing at the destination module of a send() call immediately, still within the send() call.
-
cPacket’s default getDisplayString() method now falls back to returning the encapsulated packet’s display string, instead of just returning an empty string.
-
When formatting error messages, location/time information is now placed *after* the exception text, not before. The goal was to improve readability, as user now needs to go through less blabla before getting to the actual error message. Individual error messages have also been revised for brevity and consistency (capitalization, use of quotation marks, etc.)
-
Several things have been made inspectable at runtime (e.g. from Qtenv): simulation results being collected (i.e. result filter/recorder objects added via @statistic); per-signal listeners lists; values of XML module parameters and cXMLElement trees.
-
Unit conversion now knows about C (coulomb) and related units As, mAs, Ah, mAh.
-
Ordering of 'platdep/sockets.h' and 'omnetpp.h' is no longer important. It is recommended to include 'omnetpp.h' first.
-
Changes in the Canvas API: the insertBelow()/insertAbove() methods have been added to cFigure; cFigure’s parse(cProperty*) and getAllowedPropertyKeys() methods are now public API; the first argument of the recently introduced Register_Figure() macro must now be quoted.
-
Added opp_get_monotonic_clock_usecs(). This function should be used for measuring wall-clock time intervals in schedulers and other places instead of gettimeofday() which is not monitonic.
-
opp_run (and all executable simulations) now support the '-h configvars' to print the list of dollar variables that can be used in configuration values.
-
Many other smaller-scale changes, fixes and refactoring, in part related to the ones above; see ChangeLogs under src/ for details.
Qtenv:
-
Qtenv has reached maturity and it is now the default GUI for simulations.
-
Qtenv now requires Qt5.4, and optionally OpenSceneGraph 3.2-3.5 and osgEarth 2.5-2.7.
-
You can use your own Qt bundle by setting the QT_PATH variable in configure.user before running ./configure. (This may be needed if your Linux distribution comes with an older version.)
-
Added support for smooth custom animations. This means that simulation time is interpolated between events, and the animation can be stopped between events. In the event number display, the event number is prefixed with either 'last:' or 'next:' to make it unambiguous. A new 'Animation Parameters' window has been added where one can view the current animation speed, framerate, and other metrics.
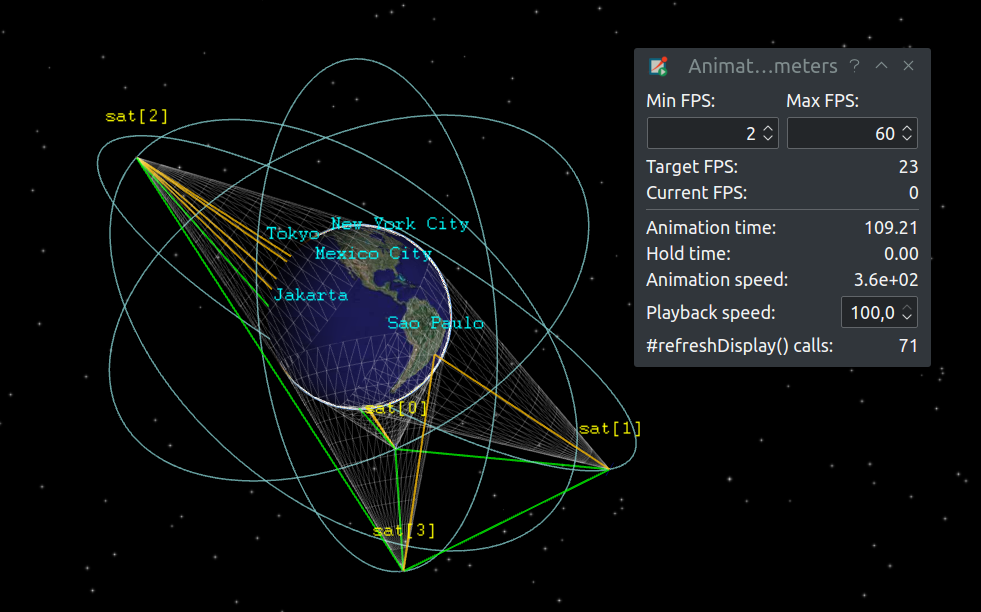
-
Added built-in support to record animation into a high quality video. Press the record button on the toolbar for instructions.
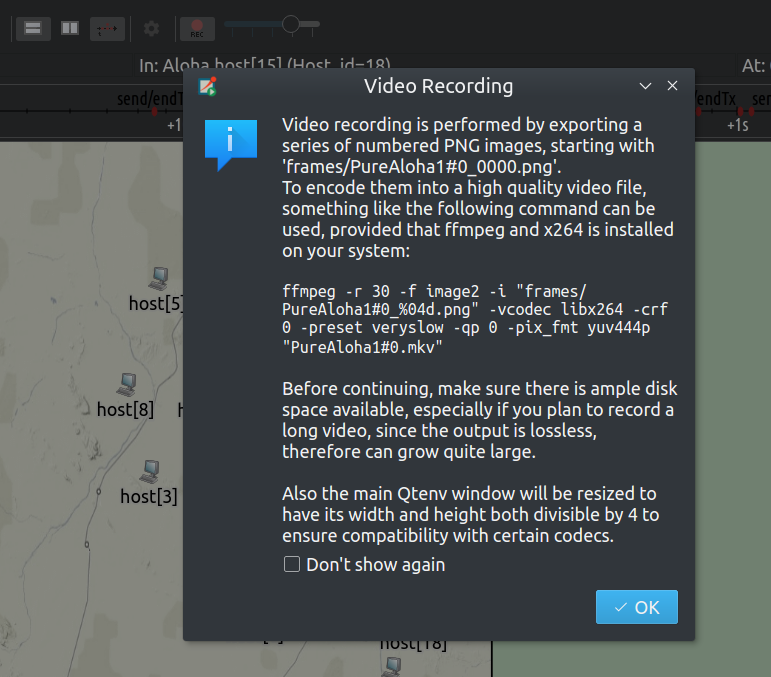
-
One-stepping now stops right before events so pressing F4 will execute the next event instantly. For consistency, after initialization, the simulation time will be set to that of the first event (not always to 0s).
-
The simulation time display now has digit grouping and units turned on by default for better readability. Settings can be changed in the context menu.

-
Added built-in support to record animation into a high quality video. (Press the record button on the toolbar for instructions.)
-
Improvements on built-in animations: Messages sent with a nonzero propagation delay are now animated properly (not instantaneously). Packets of nonzero length are now displayed as "strips" when transmitted on a link with a transmission rate and propagation delay. The animation of method call hierarchies now represents the call graph better.
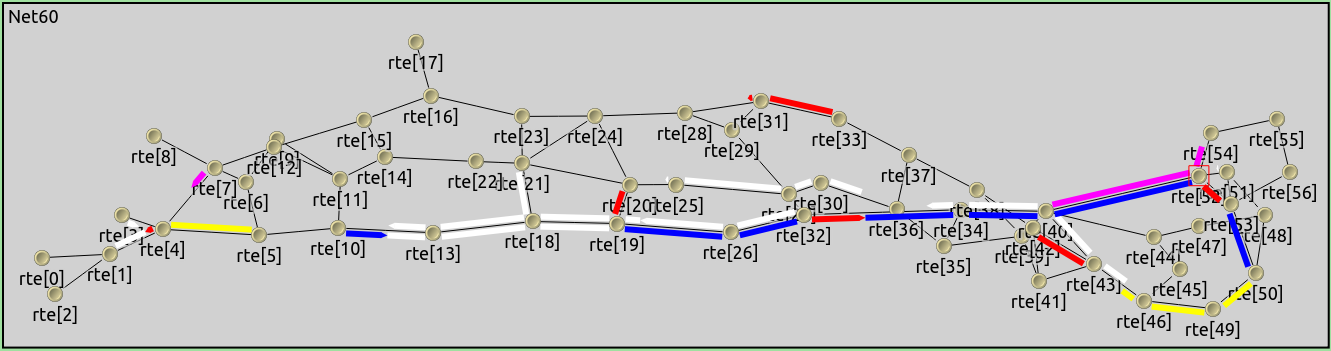
-
Two-way connections are now drawn as two half-length lines so that they don’t cover one another.
-
Module layouts are now shared among all graphical inspectors of the same module. Layout seeds are now persistent between runs.
-
The Configuration/Run selection dialog now accepts run filters from the command line and will display the matching runs on the top of the list.
-
Inspector windows made persistent between runs and will be re-opened on simulation restart.
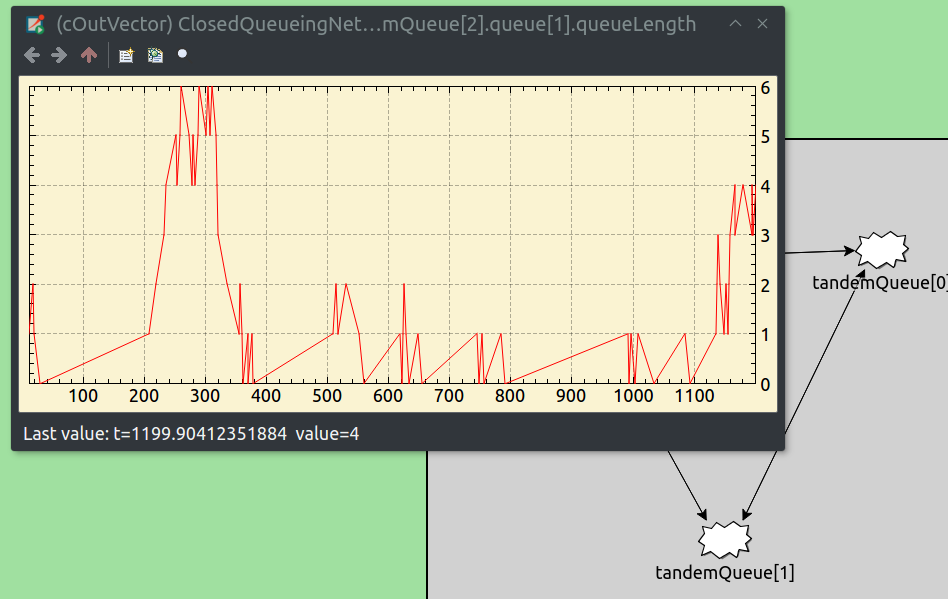
Added graphical inspectors for histograms. They are enabled for any cStatistic-based histogram objects, i.e. they are currently not available for @statistic-based output histograms.
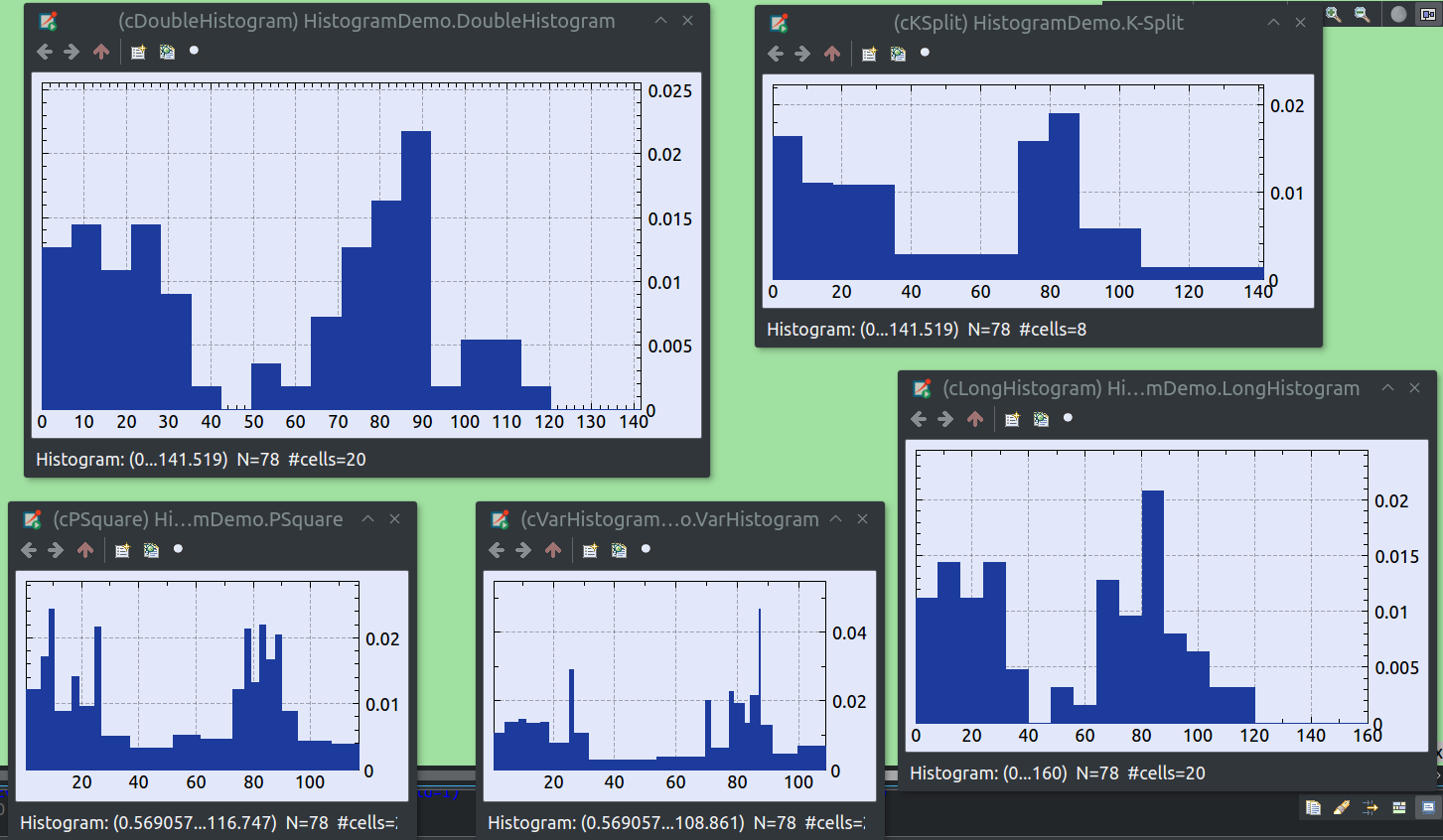
Added graphical inspectors for output vectors.
-
Other improvements, including tweaks to the Preferences dialog, context menu usability in inspectors, updated application and toolbar icons, a new 'Rebuild network' button on the toolbar, and many bug fixes.
-
Experimental support to run as a native Wayland client (start the simulation with the QT_QPA_PLATFORM=wayland environment variable set).
Tkenv:
-
While Qtenv is now the default runtime GUI, simulations can still be launched under Tkenv by adding "-u Tkenv" to the command line. Tkenv is being maintained, but it is not actively developed any more. This means that most new features, including the ones added in this OMNEST release (smooth custom animations, self-refreshing figures, etc) will not be available under Tkenv.
Envir:
-
Run filtering: The -r option of simulations now also accepts a run filter expression as an alternative to a list of run numbers and run number ranges. This makes it possible to use the values of iteration variables for filtering, instead of the artificial and more-or-less meaningless run number. The new -q option (see below) can be used to query the list of matching runs. Example: ./aloha -c PureAlohaExperiment -r '$numHosts>5 and $numHosts<10' -q runs
-
To query the list of matching runs, the new -q <what> option can be used together with -c <config> and -r <runfilter>. The argument to -q can be any of: "numruns", "runnumbers", "runs", "rundetails", "runconfig", "sectioninheritance".
-
The nesting order of iterations has been made configurable, and the default has changed: the repeat counter has been switched from being the innermost loop to being the outermost one. This is more practical, as it allows one to get early results for all data points, then refine the picture as more runs are being completed. The nesting order (also among iteration variables) can be specified using the new iteration-nesting-order configuration option.
-
Bugfix: the constraint option did not take effect when specified on the command line (--constraint=…)
-
The -s (silent, i.e. non-verbose) option has been added, partly to facilitate machine processing of -q output.
-
By default, error messages are written to stderr. A -m (merge output) option has been added that redirects errors to stdout; a practical benefit is that it preserves the relative order of the output.
-
Default result file naming scheme been changed to be more practical. The traditional naming scheme contained the run number, which has now been replaced by the values of the iteration variables and the repetition counter. Example: old: Aloha-16.sca, new: Aloha-numHosts=10,mean=0.9-#3.sca. Illegal and inconvenient characters are encoded in an urlencode-like manner. This naming scheme applies to cmdenv output files, eventlog files and snapshot files as well.
-
Experimental support for SQLite as result file format. SQLite result files can be browsed using existing GUI tools (SQLite Browser, SQLite Studio), can be queried using SQL, and can be accessed and manipulated from all major programming languages including Python and R. These benefits are in exchange for slight performance penalty. SQLite result files contain the same information as OMNEST native result files, they can co-exist, and OMNEST tools and the IDE understand both. To switch to SQLite as default result file format, compile OMNEST with PREFER_SQLITE_RESULT_FILES=yes set in configure.user. To use SQLite only for specific simulations, add the following lines to their omnetpp.ini files:
outputvectormanager-class="omnetpp::envir::SqliteOutputVectorManager" outputscalarmanager-class="omnetpp::envir::SqliteOutputScalarManager"
-
In output scalar files, when run attributes (iteration variables, etc.) are saved as scalars, the module name they are saved with has been changed from "." to "_runattrs_".
-
The cpu-time-limit option has been fixed to work as expected; a new real-time-limit option also has been added.
Cmdenv:
-
All changes described in the Envir section above apply, plus:
-
When performing multiple runs, Cmdenv now stops after the first run that stops with an error. This behavior can be controlled with the new cmdenv-stop-batch-on-error=<bool> option.
-
When performing multiple runs, Cmdenv now prints run statistics at the end. Example output: "Run statistics: total 42, successful 30, errors 1, skipped 11"
-
The cmdenv-output-file option can now be specified per run, and now has a default file name that follows the naming scheme of result files (but with the .out extension). Since saving the output can no longer be disabled by omitting the cmdenv-output-file setting, new option cmdenv-redirect-output=<bool> has been added for that purpose.
-
The cmdenv-interactive option can now be specified on per-run basis.
Tools:
-
scavetool: The command-line interface (options and help) has been redesigned for usability.
-
scavetool: The tool now supports querying the contents of result files in a user-friendly way, via the new "query" subcommand. This subcommand has also been made the default operation mode. For example, a simple "scavetool *.vec *.sca" command reports the number of runs, vectors and scalars found in the specified files.
-
scavetool: CSV and other tabular export has been improved: run attributes (iteration variables, etc) are now added to the output as columns. Note that scavetool currently cannot export to SQLite.
-
opp_makemake: OMNEST and generated model makefiles now use compiler- generated dependencies (gcc/clang -MMD option) that are saved in the out/ directory in *.d files. "make depend" is no longer needed.
-
opp_makemake: Support for deep includes (automatically adding each subfolder to the include path) has been dropped, due to being error-prone and having limited usefulness. In projects that used this feature, #include directives need to be updated to include the directory as well.
-
opp_makemake: Removed support for generating nmake-compatible makefiles, as we now use GNU Make on all platforms.
-
opp_featuretool: Symbols for enabled features (e.g. WITH_IPv4 for the IPv4 feature in INET) are now placed into a generated header file, instead of being passed to the compiler via -D options. The name of header file can be specified in the feature definition file (.oppfeatures).
-
opp_runall has been reimplemented in Python, and its command-line interface has been redesigned to not only allow using multiple CPUs but also several runs per Cmdenv instance. (This change allows one to execute a large number of short simulation efficiently by reducing process startup overhead.) Internally, opp_runall now uses the new "-q" option of simulations to expand a run filter expression to a list of runs.
-
opp_test: export "run" script and "retest" scripts under work/ for each test, to facilitate running tests manually. Minor bug fixes.
-
Removed unused utilities like opp_makedep, lcg32_seedtool, abspath, and some others.
-
scavetool: the -f option for the 'query' command adds statistics fields (min, max, sum, etc.) as scalars.
-
msgc: Message compiler now correctly generates 'override' keywords for certain functions.
-
The message compiler now generates code which produces no warnings even when -Wall -Wextra -Wpedantic is used as a compiler command line option.
IDE:
-
The IDE is now based on Eclipse 4.6.3 Neon and CDT 9.2.1 (Java 1.8 required).
-
Fixed an issue when generating NED documentation on Windows
IDE/C++ Build:
-
The "Collecting includes…" phase of project build (that could take quite a significant amount of time, and was often seen as a pain point) has been eliminated. The key was to switch from IDE-generated dependencies to compiler-generated dependencies (see corresponding opp_makemake change) that made include analysis in the IDE redundant.
-
Change in "Project Features" feature: Preprocessor symbols for enabled features (e.g. the WITH_IPv4 macro for the IPv4 feature) are now placed into a generated header file, and not added to the build configuration (Paths & Symbols page) as macros to be passed to the compiler via -D options. The name of header file is part of the feature definition file (.oppfeatures). Using a generated header file reduces the number of things that can go wrong during indexing and project build, and also has the advantage of being seen from derived projects.
-
The "Export build tester makefile" button has been removed from the Project Features property page. The INET Framework project now has an opp_featuretool-based shell script for the same purpose (tests/featuretest) that can be easily adapted to other projects as well.
-
Support for deep includes (automatically adding each subfolder to the include path) has been dropped from the IDE as well, due to being error- prone and having limited usefulness.
-
Improvements in the Makemake Options dialog that opens from the Makemake project property page. For example, an "Include directories" listbox has been added to the Compile tab page, and less frequently used options on the same page have been moved under the More>>> link.
-
CDT integration: renamed the default C/C++ project configuration names from "gcc-debug"/"gcc-release" to simply "debug" and "release".
- IDE can now generate a makefile that is exactly the same as the one generated by the opp_makemake tool.
IDE/Simulation Launching:
-
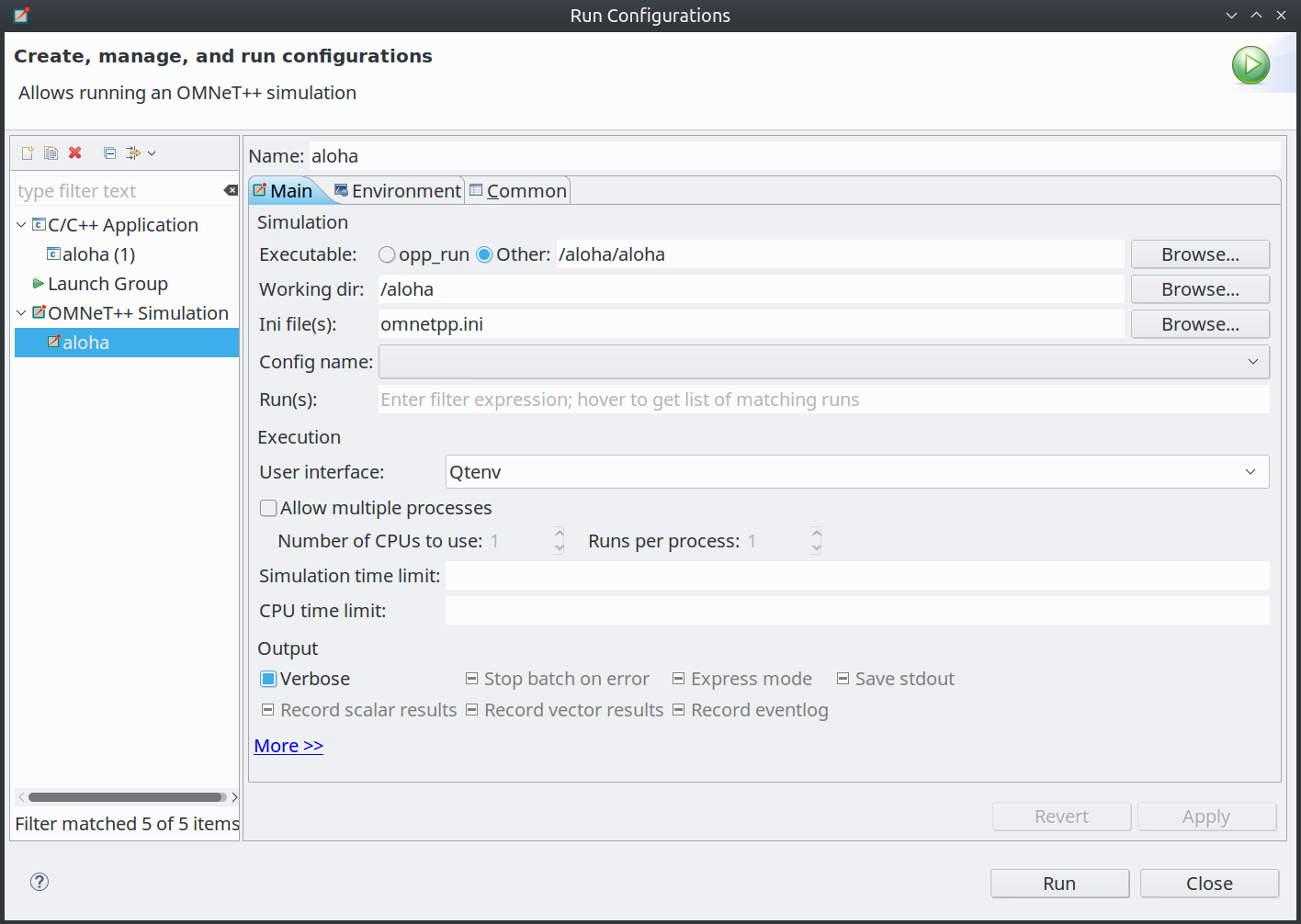
In the Run/Debug Configurations dialog, the "OMNEST Simulation" form page has been revised for usability and to better support simulation campaigns. The launcher (code that schedules and actually runs the simulations and arranges feedback in the Progress view and the Console) has also been improved. Details follow.
-
The "Runs" form field now accepts a run filter expression that can refer to iteration variables. (This form field corresponds to the -r option of simulations.)
-
Batch execution of simulations is now controlled with two new spinner widgets: "Number of CPUs to use", "Runs per process".
-
The form page now allows specifying time limits for the simulation ("Simulation time limit", "CPU time limit" fields)
-
Radio buttons have been replaced by tri-state checkboxes (with on/off/grayed states, where the grayed state means "no setting specified, let the inifile setting take effect".) The consequent space saving allowed other options to be added to the form page: "Verbose", "Stop batch on error", "Express mode", "Save stdout", "Record scalar results", "Record vector results", "Record eventlog".
-
User interface selection now also uses an editable combo instead of radio buttons.
-
Added content assist for Additional Arguments field.
-
Improvements in the launcher: Simulation batches are now easier to cancel; in case of a simulation error, the error dialog now correctly displays the error message, not just a "Finished with error" text.
IDE/Inifile Editor:
-
Updated to know about option changes and new options.
IDE/Analysis Tool:
-
In the Browse Data page, display Experiment/Measurement/Replication columns instead of Folder/Filename/RunId/Config/RunNumber. Note that this is just the default value for a preference, so the change will only take effect in new installations or new workspaces. The default columns widths have also been increased.
-
Initial support for SQLite result files. From the end user perspective, they should work exactly as OMNEST result files.
-
CSV and other tabular export has been improved in the same way as in scavetool (as they use the same export engine).
Build:
-
The Windows version now targets 64-bit Windows, using MinGW-w64. The required GCC compiler is included as well as all necessary libraries (Qt5, OSG, etc.) Support for 32-bit Windows has been dropped.
-
Compiling OMNEST now requires a C++11 compliant compiler.
-
The configure script no longer detects and tests for the presence of the 'pcap' library. If models need it, they have to implement their own method to detect and configure it.
-
omnetpp.h is now treated as a 'system header', so it will no longer generate warnings in case a model specifies more stringent checking for the compiler.
-
The 'configure' script now accepts WITH_XXX=yes/no options on the command line. Look into the configure.user file to see the supported variables.
-
Cross compilation of OMNEST for Windows on a Linux host is now supported.
Documentation:
-
Install Guide has been updated and covers the installation procedure on the most recent operating system versions.
-
The Simulation Manual has been heavily updated. Look for the (new) symbol to see the updated content.
-
User Guide now has a new chapter about the Qtenv runtime environment.
Samples:
-
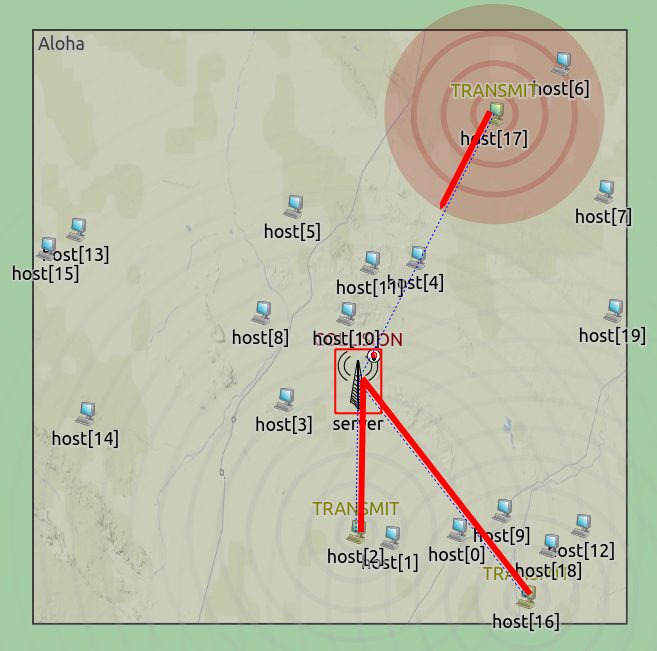
aloha: The updated example highlights the use of the new smooth animation API. The server and all hosts now have fixed positions (still random but deterministic, and not using auto-layouting), so that their individual propagation delays can be computed. Each transmitted packet is visualized with a ring and many concentric circles, illustrating the propagation of the electromagnetic wave. The visualization is faithful, e.g. multiple signals visually overlapping at a receiver actually means a collision. Animation speed is controlled by each node, taking three parameters for different states (idle, transmission edge, midtransmission) into account.
- The routing example was modified to demonstrate the new, built-in packet animation in Qtenv. Packets are displayed as arrows along the connection showing the actual packet length on the wire.
-
osg-satellites: Refactored mobility logic and replaced the discontinued MapQuest public tile source with a single offline image to avoid dependency on external sources.
-
queueinglib: Fixed a race condition by requiring the PassiveQueue to allocate the Server before sending a job to it.
-
resultfiles: Result files were renamed to reflect the new default naming scheme (i.e. configname-itervars-#repetition).
-
osg-earth: Made the mobile nodes in the 'Boston streets' configuration more easily noticeable by increasing their sizes, and adding a color parameter. Movement trails have been raised off the ground a bit to avoid Z-fighting glitches. The example now has a configuration where off-line map tiles are used instead of an on-line map tile provider. (Note that this may not work on current Debian/Ubuntu distros, because they contain an osgEarth library version that is too old.)


